
An abstract data type is abstraction of data structure
- which provides only interface ,to which data structure must adhere to .The details of how it is to be implemented are not mentioned.
E.g List,Queue,Map etc
Big Theta | Big Omega | Big Oh Notation ?
Big Oh only cares about worst case
How much time this algorithm needs to finish ?
How much space this algorithm needs for computation ?
Big only cares about when n goes too big
n3 + n2 + 2n + 1... O(n3)
_______________________________________________
1.Arrays
- Most widely fixed length container of indexable objects where n is number of elements that can be stored
- Static length
- indexable data structure , each element can be referenced by index
- Contigous piece of memory
Where to use arrays?
- Storing and accessing elements
- For buffers in I/O routine
- Look up table
- Can be used to return multiple values from function
- Dynamic programming
Access: O(1) As they are indexed
Search:O(n) Worst case(last element or not present
Insertion : N/A
Deletion: N/A
Append: N/A
As they are fixed length
What is Dynamic array?
a) Using static arrays
Where to use Dynamic array?
Complexity
Access: O(1)
Search:O(n)
Insertion : O(n) [you have to shift all the elements]
Deletion: O(n)[you have to shift all the elements]
Append :O(1)[you have to add elements to end]
____________________________________________________________________
2.Linked List
What is linked list?
Sequential list of nodes ,where each node holds data & points to another node ,with last node pointing to null
Where are linked list used?
- Implementation of STACKS AND QUEUES
- Implementation of Circular List
- Modeling real world data such as train or DNA Sequences
- Separate chaining in Hashtable/HashMaps to avoid collisons
- Implementation of adjacency list in Graphs
Access: O(1)
Search:O(n)
Insertion : O(n) [you have to shift all the elements]
Deletion: O(n)[you have to shift all the elements]
Append :O(1)[you have to add elements to end]
_____________________________
3.Stack
What is stack?
Stack is a one ended linear data structure which models real world objects
Operations:
push
pop
peek
Implementation
- using list
- using arrays
Where to use stack?
- Is Used Behind the scene in keeping recursive calls
- Is Used in text editors for undo operations
- Is Used in maths expression to verify closing & opening braces
- is used in DFS/Depth first on graph
Complexity of stack depends on implementation?
Linked list implementation : Complexity
Pushing :
Popping :
Peeking :
Searching
Size:
Array implementation : Complexity
Pushing:
Popping :
Peeking :
Searching
Size :
Common problems using STACK
- Brackets expression validation
- Tower of Hanoi
__________________________________________
4.Queue
4.What is queues?
Real world data structure with two primary operations
Enqueue/Add/Offer
Dequeue/Remove/polling
Where to use queues?
- Line at shopping counter/Bus stop
- FIFO algorithms
- BFS alhorithm
Complexity
- Enqueue o(1)
- Dequeue o(1)
- Peeking o(1)
- isEmpty = contains o(n)
- Removal = o(n)
_________________________________________
5.Priority Queues
What is priority queues?
What is priority queues?
- Abstract data type,where each element has a priority associated with it.
- Priority of elements determines order in which elements can be removed
- They support comparable data
when are they useful ?
________________________________________
6.Heap
What is Heap ?
What is Heap ?
A heap is a tree based DS,which satisfies heap invariant or heap property ,which is parents are always in order with its child.
Are duplicate values allowed in Heap ?
Yes as long it follow any of the property min heap or max they do
7.Where are Heaps/Priority Queue used ?
- In graph algorithms such as
- Dijkstara's uses Heap/Priority Queue
- Huffman coding uses Heap
- BFS uses priority Queue
- Prim's MST uses priority queue
Complexity
- Heap Construction O(n)
- Polling O(log(n))
- Peeking O(1)
- Adding O(log(n))
There are many types of heaps
- Binary Heap
- Fibonacci heap
- Pairing Heap
- Binomial Heap
_______________________________________________________________
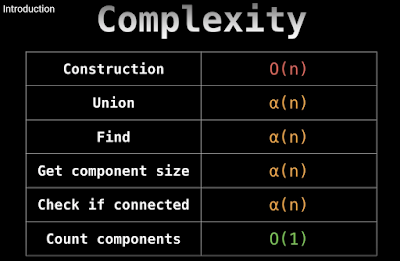
8.Union Find
What is Union Find ?
What is Union Find ?
It is a data structure that keeps track of elements which are split into one or more disjoint sets.It has two primary operations:
find and union.
- Kruskal's minimum spanning algorithm
- Grid percolation
- Network connectivity
- Least common ancestor of trees
- Image processing
Applications of Union -Disjoint Sets
- Least Common Ancestor in Trees
- Network Connectivity
- Grid Percolation
- Image processing
- Krushal's Minimum Spanning Tree
________________________________________
9.HashMap/HashTableWhat is HashMap?
Data structure which provides
- mapping for key value pair using technique called hashing
Properties of HashMap
Collision Methods
Separate Chaining
Implementation : Linked list /Binary trees/ Arrays
Open Addressing
Linear Probing
Quadratic Probing
Double Hashing
_https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/lectures/34HashTables.pdf_
__________________________________________
10.Tree
What is Tree ?
- is an undirected graph
- acyclic in nature
- n nodes connected with n-1 edges
- any two vertices are connected through only one path
Applictaions
- implementation of some map an ADTs
- Red Black Trees
- AVL Trees
- Splay Trees
Syntax trees
Treap - a probabilistic DS (uses randomized BST)
How to insert/delete/traverse(pre/in/post/level)order a node in BST?
Binary Search Tree
_____________________________________________
GRAPHS
_____________________________________________
FENWICK TREES (BINARY INDEXED TREES)
SSS
_____________________________________________
SUFFIX ARRAYS
PROBLEMS:-
- LONGEST COMMON PREFIX
- SUFFIX ARRAY FINDING SUBSTRING









No comments:
Post a Comment